ISO 50001 - Energy management system
Lo standard specifica i requisiti per creare, avviare, mantenere e migliorare un sistema di gestione dell'energia. L'obiettivo di tale sistema è di consentire che un'organizzazione persegua, con un approccio sistematico, il miglioramento continuo della propria prestazione energetica comprendendo in questa l'efficienza energetica nonchè il consumo e l'uso dell'energia.
Definisce, inoltre, i requisiti applicabili all'uso e consumo dell'energia, includendo l'attività di misurazione, di documentazione e di reportistica, di progettazione e d'acquisto per le attrezzature, i processi e il personale che contribuiscono alla definizione della prestazione energetica.
Si applica a tutti i fattori che concorrono a determinare la prestazione energetica e che possono essere controllati e influenzati dall'organizzazione. La norma però non definisce specifici criteri di prestazione energetica.
La norma è stata sviluppata per essere utilizzata in maniera indipendente anche se può essere integrata con altri sistemi di gestione.
E'applicabile ad ogni organizzazione che desideri assicurarsi di essere conforme alla propria politica energetica e dimostrare tale conformità ad altri mediante autovalutazione e autodichiarazione di conformità o mediante certificazione di terza parte del proprio sistema di gestione dell'energia. La norma fornisce inoltre delle linea guida per il suo utilizzo.
ISO 50001:2011(en)
Energy management systems - Requirements with guidance for use
UNI CEI EN ISO 50001:2011
Sistemi di gestione dell'energia - Requisiti e linee guida per l'uso
La presente norma è la versione ufficiale della norma europea EN ISO 50001 (edizione ottobre 2011) e tiene conto delle correzioni introdotte il 25 gennaio 2012 (EC 1-2012 UNI CEI EN ISO 50001:2011).
Update 27 Novembre 2017
Draft ISO 5001 vers. 2018
Come tutti gli standard internazionali, ISO 50001 è stato sottoposto a revisione periodica per garantire che continui a soddisfare le esigenze in rapida evoluzione del settore energetico.
Questo lavoro viene svolto dal comitato tecnico ISO responsabile della gestione energetica e del risparmio energetico (ISO/TC 301), il cui segretariato è detenuto da ANSI , membro ISO per gli Stati Uniti, in un accordo di gemellaggio con il membro ISO per la Cina, SAC . Di seguito, si riportano i principali cambiamenti con l'aiuto di Deann Desai, professore al Georgia Institute of Technology e Convenor del gruppo di lavoro incaricato di rivedere lo standard.
"Forse il cambiamento più importante per la versione 2018 è l'incorporazione della struttura di alto livello, che fornisce una migliore compatibilità con altri standard del sistema di gestione." La struttura di alto livello (HLS) è un concetto semplice ed efficace. "Poiché le organizzazioni spesso implementano una serie di standard per i sistemi di gestione, l'uso di una struttura condivisa, così come molti degli stessi termini e definizioni, aiuta a mantenere le cose semplici", spiega il Prof. Desai. Ciò è particolarmente utile per le organizzazioni che scelgono di gestire un singolo sistema di gestione (a volte chiamato "integrato") in grado di soddisfare contemporaneamente i requisiti di due o più standard del sistema di gestione .
Il Prof. Desai prosegue: "Ci sono altri miglioramenti nella versione 2018 per aiutare a garantire che i concetti chiave relativi alle prestazioni energetiche siano chiari per le piccole e medie imprese (PMI)." Questo è importante per incoraggiare l'adozione dell'uso della gestione standard di sistema da parte delle PMI, che a volte presumono che i benefici degli standard internazionali si applichino soprattutto alle imprese multinazionali.
Con l'efficienza energetica che gioca un ruolo chiave nel raggiungimento degli obiettivi sociali e ambientali per tutte le dimensioni aziendali, promuovere l'adozione della ISO 50001 è anche una parte importante del lavoro del Prof. Desai. Diverse iniziative che hanno contribuito ad aumentare l'uso della ISO 50001 in tutto il mondo, tra cui il Clean Energy Ministerial (CEM) e l'Organizzazione delle Nazioni Unite per lo sviluppo industriale (UNIDO).
The Clean Energy Ministerial è un programma globale di premi che riconosce le organizzazioni leader per i loro risultati nella gestione energetica e l'uso della ISO 50001 per affrontare le sfide energetiche e climatiche. Le organizzazioni certificate ISO 50001 sono invitate a presentare casi di studio per il riconoscimento.
La bozza di norma internazionale ISO/DIS 50001 è stata approvata a novembre 2017 e la nuova versione di ISO 50001 dovrebbe essere pubblicata nel 2018.
__________
Preview ISO 50001:2011(en) Energy management systems - Requirements with guidance for use
Foreword
ISO (the International Organization for Standardization) is a worldwide federation of national standards bodies (ISO member bodies). The work of preparing International Standards is normally carried out through ISO technical committees. Each member body interested in a subject for which a technical committee has been established has the right to be represented on that committee. International organizations, governmental and non-governmental, in liaison with ISO, also take part in the work. ISO collaborates closely with the International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC) on all matters of electrotechnical standardization.
International Standards are drafted in accordance with the rules given in the ISO/IEC Directives, Part 2.
The main task of technical committees is to prepare International Standards. Draft International Standards adopted by the technical committees are circulated to the member bodies for voting. Publication as an International Standard requires approval by at least 75 % of the member bodies casting a vote.
Attention is drawn to the possibility that some of the elements of this document may be the subject of patent rights. ISO shall not be held responsible for identifying any or all such patent rights.
ISO 50001 was prepared by Project Committee ISO/PC 242, Energy Management.
Introduction
The purpose of this International Standard is to enable organizations to establish the systems and processes necessary to improve energy performance, including energy efficiency, use and consumption. Implementation of this International Standard is intended to lead to reductions in greenhouse gas emissions and other related environmental impacts and energy cost through systematic management of energy. This International Standard is applicable to all types and sizes of organizations, irrespective of geographical, cultural or social conditions. Successful implementation depends on commitment from all levels and functions of the organization, and especially from top management.
This International Standard specifies energy management system (EnMS) requirements, upon which an organization can develop and implement an energy policy, and establish objectives, targets, and action plans which take into account legal requirements and information related to significant energy use. An EnMS enables an organization to achieve its policy commitments, take action as needed to improve its energy performance and demonstrate the conformity of the system to the requirements of thisInternational Standard. This International Standard applies to the activities under the control of the organization, and application of this International Standard can be tailored to fit the specific requirements of the organization, including the complexity of the system, degree of documentation, and resources.
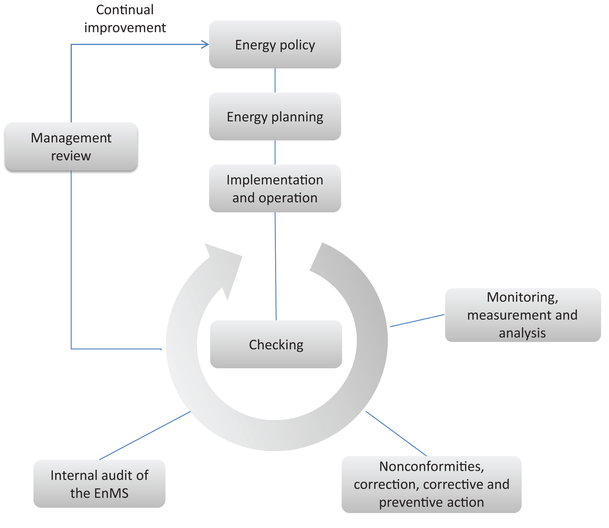
This International Standard is based on the Plan - Do - Check - Act (PDCA) continual improvement framework and incorporates energy management into everyday organizational practices, as illustrated in Figure 1.
NOTE In the context of energy management, the PDCA approach can be outlined as follows:
- Plan: conduct the energy review and establish the baseline, energy performance indicators (EnPIs), objectives, targets and action plans necessary to deliver results that will improve energy performance in accordance with the organization's energy policy;
- Do: implement the energy management action plans;
- Check: monitor and measure processes and the key characteristics of operations that determine energy performance against the energy policy and objectives, and report the results;
- Act: take actions to continually improve energy performance and the EnMS.
Figure 1 — Energy management system model for this International Standard
NOTE Annex B shows the relationship between this International Standard and ISO 9001:2008, ISO 14001:2004 and ISO 22000:2005.
This International Standard specifies requirements for establishing, implementing, maintaining and improving an energy management system, whose purpose is to enable an organization to follow a systematic approach in achieving continual improvement of energy performance, including energy efficiency, energy use and consumption.
This International Standard specifies requirements applicable to energy use and consumption, including measurement, documentation and reporting, design and procurement practices for equipment, systems, processes and personnel that contribute to energy performance.
This International Standard applies to all variables affecting energy performance that can be monitored and influenced by the organization. This International Standard does not prescribe specific performance criteria with respect to energy.
2 Normative references
ISO 50001 - Energy management systems
Year of publication: 2016 | Edition: 1 (in allegato)
Learn more about ISO's standard for helping organizations manage their energy performance.
...
ISO 50001 - Energy management systems - A practical guide for SMEs
Year of publication: 2015 | Edition: 1
Designed to be used alongside ISO 50001, this handbook provides concrete examples and guidance for SMEs implementing energy efficiency measures, without the need for investment in new technology or systems.
Preview in allegato.
Fonte:
ISO
UNI
Articoli collegati:























1 Scope