IEC 61882:2016 Examples of HAZOP studies / CEI EN 61882:2017
ID 15472 | 17.01.2022 / Examples of HAZOP studies Annex B IEC 61882:2016 (CEI 2017)
IEC 61882:2016 Hazard and operability studies (HAZOP studies) - Application guide
L’HAZard and OPerability analysis (HAZOP) è una tecnica (metodologia di Analisi dei Rischi) molto utilizzata in ambienti industriali con tecniche di controllo automatico di processo, in particolare nell'industria chimica.
Il metodo di Analisi di Pericolo e Operabilità (o metodo HAZOP, dall’inglese HAZard and OPerability analysis) ha lo scopo di individuare i rischi presenti in un processo produttivo. Oggi è uno dei metodi più utilizzati per identificare i rischi, in quanto è una procedura molto strutturata che, oltre a individuare eventuali deviazioni dal processo standard, si occupa anche di valutare interventi correttivi e risolutivi.
Nel presente elaborato viene riportato un estratto dell’Allegato B della norma IEC 61882:2016 contenente esempi di applicazione del metodo HAZOP.
Examples of HAZOP studies
B.1 General
B.2 Introductory example
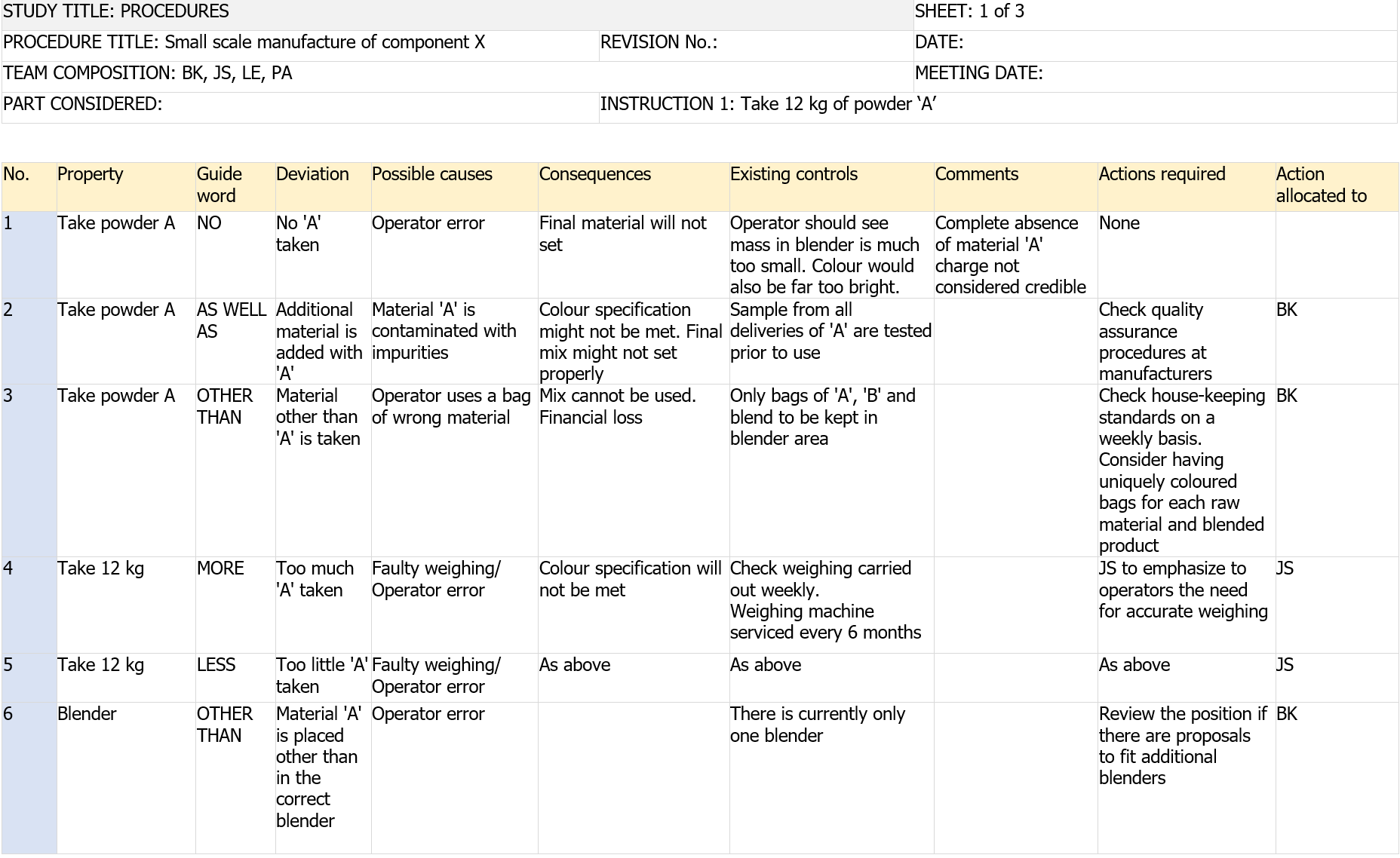
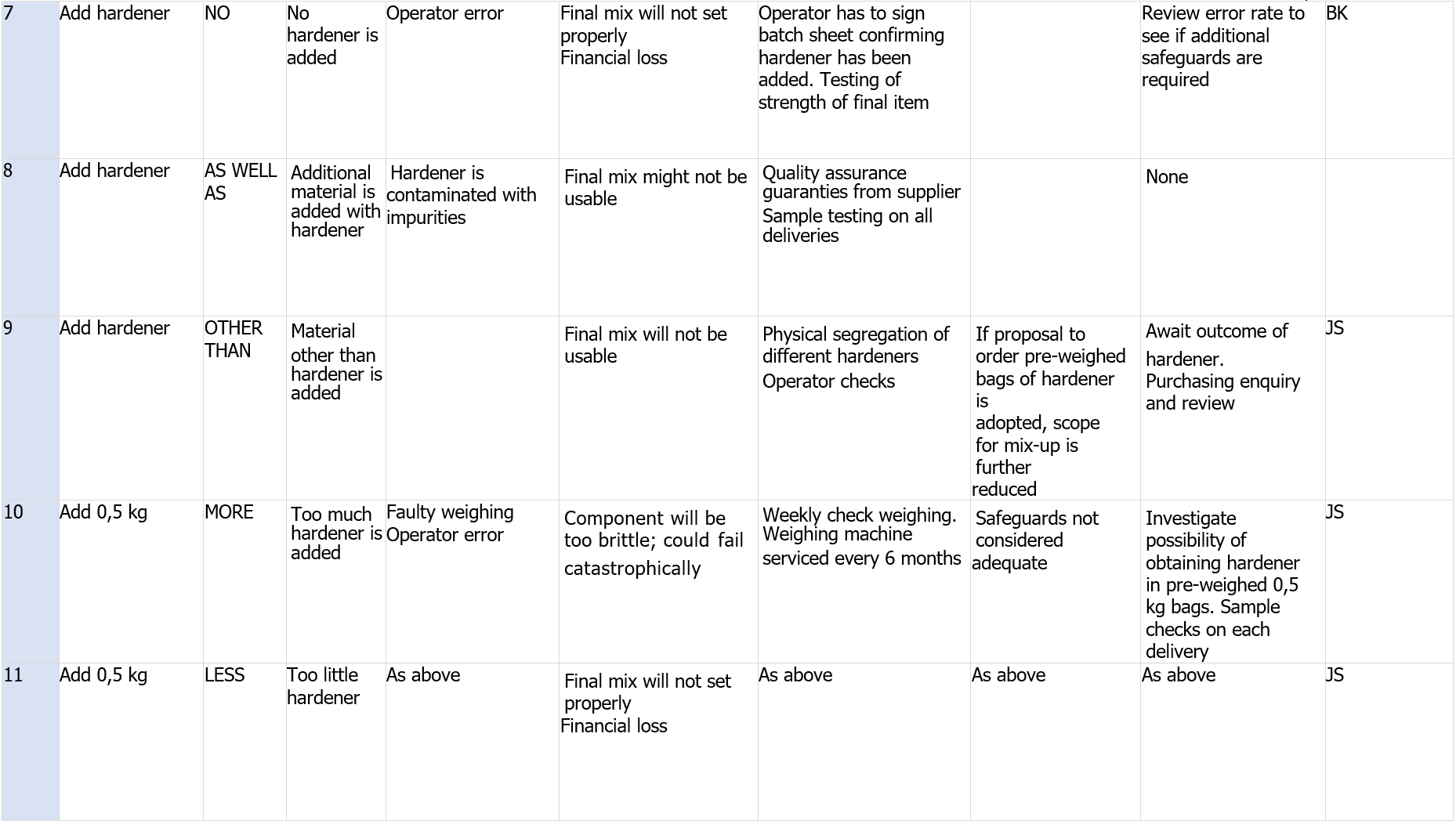
B.3 Procedures
B.4 Automatic train protection system
B.4.1 General
B.4.2 Application
B.5 Example involving emergency planning
B.6 Piezo valve control system
B.7 HAZOP of a train stabling yard horn procedure
Figure 1 – The HAZOP study procedure
Figure 2 – Flow chart of the HAZOP examination procedure – Property first sequence
Figure 3 – Flow chart of the HAZOP examination procedure – Guide word first sequence
Figure B.1 – Simple flow sheet
Figure B.2 – Train-carried ATP equipment
Figure B.3 – Piezo valve control system
Table 1 – Example of basic guide words and their generic meanings
Table 2 – Example of guide words relating to clock time and order or sequence
Table 3 – Examples of deviations and their associated guide words
Table B.1 – Properties of the system under examination
Table B.2 – Example HAZOP worksheet for introductory example
Table B.3 – Example HAZOP worksheet for procedures example
Table B.4 – Example HAZOP worksheet for automatic train protection system
Table B.5 – Example HAZOP worksheet for emergency planning
Table B.6 – System design intent
Table B.7 – Example HAZOP worksheet for piezo valve control system
Table B.8 – Operational breakdown matrix for train stabling yard horn procedure
Table B.9 – Example HAZOP worksheet for train stabling yard horn procedure
IEC 61882:2016 provides a guide for HAZOP studies of systems using guide words.
This is a structured and systematic technique for examining a defined system, with the objectives of:
- identifying risks associated with the operation and maintenance of the system. The hazards or other risk sources involved can include both those essentially relevant only to the immediate area of the system and those with a much wider sphere of influence, for example some environmental hazards;
- identifying potential operability problems with the system and in particular identifying causes of operational disturbances and production deviations likely to lead to nonconforming products.
An important benefit of HAZOP studies is that the resulting knowledge, obtained by identifying risks and operability problems in a structured and systematic manner, is of great assistance in determining appropriate remedial measures.This second edition cancels and replaces the first edition published in 2001.
This edition constitutes a technical revision.
This edition includes the following significant technical changes with respect to the previous edition:
- clarification of terminology as well as alignment with terms and definitions within ISO 31000:2009 and ISO Guide 73:2009;
- addition of an improved case study of a procedural HAZOP. Keywords: HAZOP, risks and operability problems
Pubblication date: 10.03.2016
La norma IEC 61882:2016 (CEI 2017) fornisce una guida per gli studi di sistemi HAZOP che utilizzano parole guida.
Essa fornisce una guida sulla applicazione della tecnica e procedura di studio HAZOP, compresa la definizione, la preparazione, le sessioni d'esame e la documentazione risultante e follow-up.
Sono anche previsti esempi di documentazione, ed una vasta gamma di esempi che comprendono diverse applicazioni, che illustrano gli studi HAZOP.
L’Ed. 2016 costituisce una revisione tecnica della precedente 2001 e include le seguenti modifiche tecniche significative:
- Chiarimento della terminologia, nonché l'allineamento con i termini e le definizioni all'interno di ISO 31000:2009 e ISO Guide 73:2009;
- Aggiunta di un caso di studio migliorato di un HAZOP procedurale.
_________
Annex B (informative)
Examples of HAZOP studies
B.1 General
The purpose of the examples contained in Annex B is to illustrate how the principles of a HAZOP study, outlined in this standard (particularly in 4.2, 6.3 and 6.4) are applied to a range of applications encompassing various industries and activities. It should be noted however that the examples have been simplified significantly for illustrative purposes and do not purport in any way to reproduce all the detailed technical complexity of real case studies. It should also be noted that only sample outputs are provided.
B.2 Introductory example
The purpose of this example is to introduce the reader to the basics of the HAZOP examination method. The example is adopted from one given in the original publication on HAZOP studies.
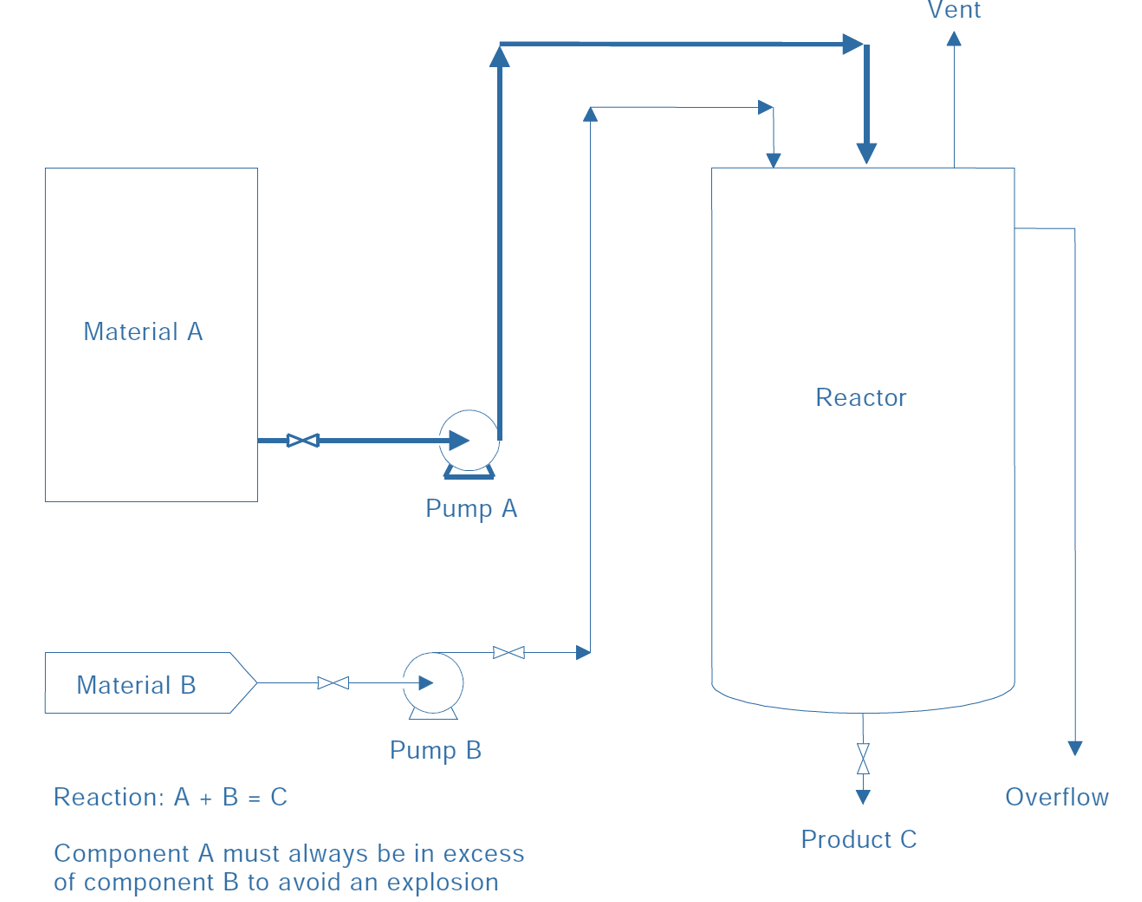
Consider a simple process plant, shown in Figure B.1. Materials A and B are continuously transferred by pumps from their respective supply tanks to combine and form a product C in the reactor. Suppose that A always has to be in excess of B in the reactor to avoid an explosion hazard. A full design representation would include many other details such as the effect of pressure, reaction and reactant temperature, agitation, reaction time, compatibility of pumps A and B, etc. but for the purposes of this simple illustrative example they will be ignored. The part of the plant being examined is shown in bold
Figure B.1 - Simple flow sheet
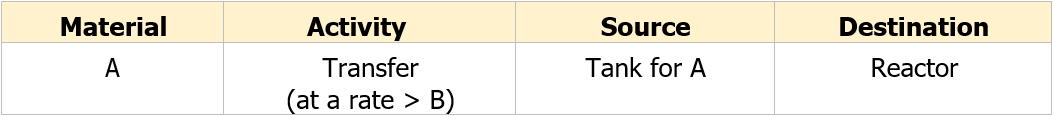
The part of the system selected for examination is the line from the supply tank holding A to the reactor, including pump A (see Table B.1). The design intent for this part is to continuously transfer material A from the tank to the reactor at a rate greater than the transfer rate of material B. In terms of the properties suggested in 4.2, the design intent is given in the previous paragraph of Clause B.2.
Table B.1 - Properties of the system under examination
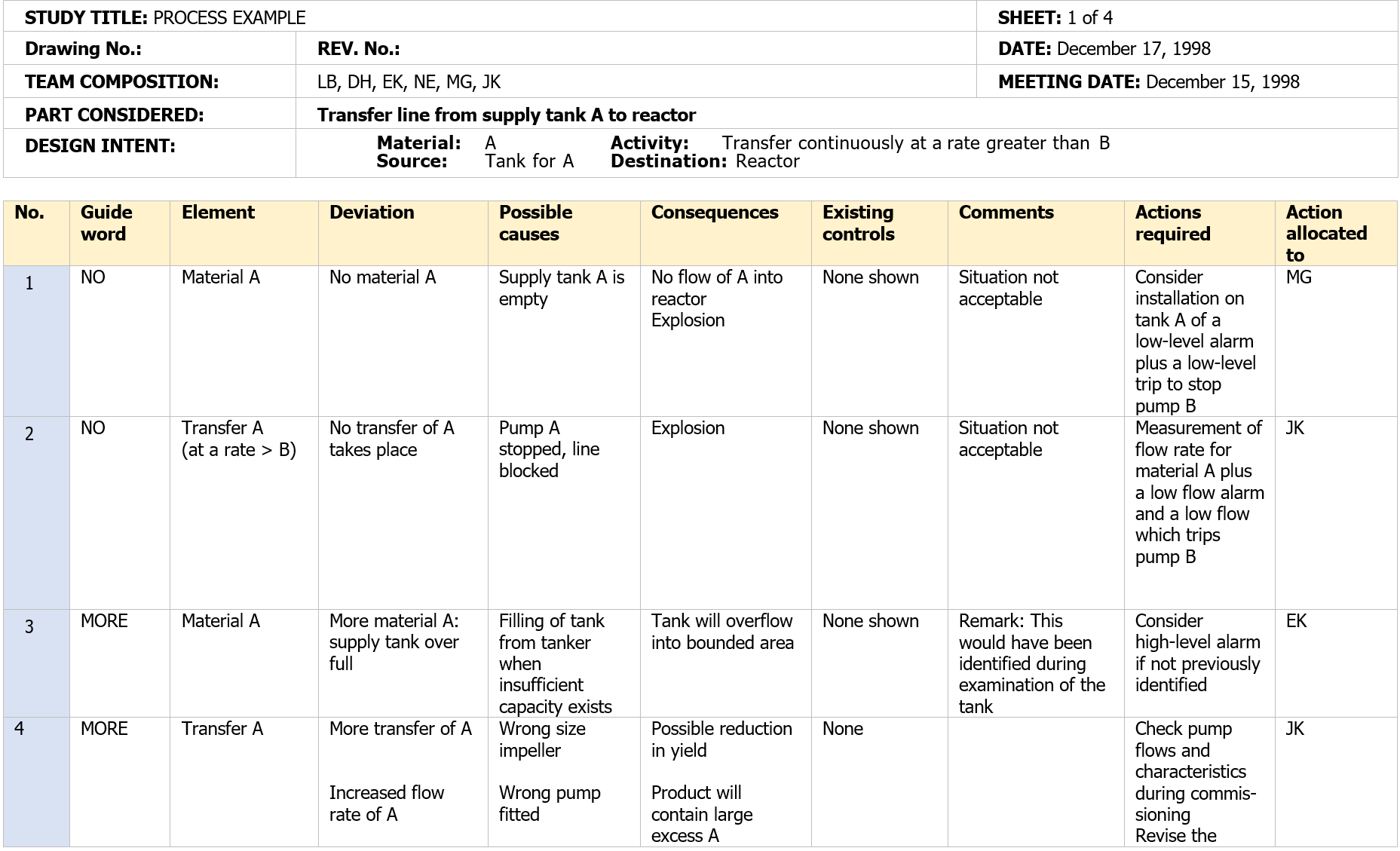
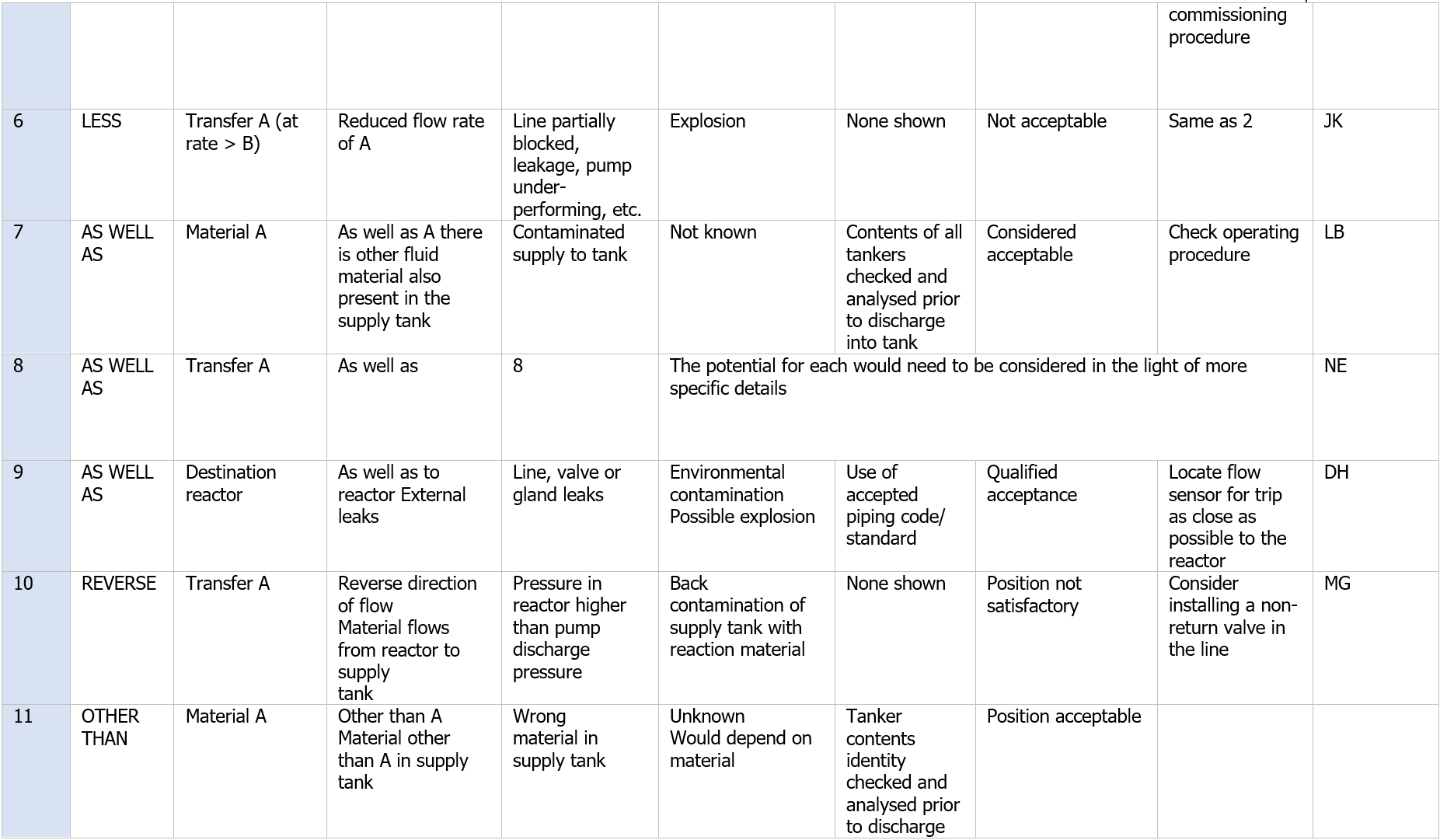
Each of the guide words indicated in Table 3 (plus any others agreed as appropriate during the preparatory work, is then applied to each of these properties in turn and the results recorded on HAZOP worksheets. Examples of possible HAZOP outputs are indicated in Table B.2, where the 'by exception' style of reporting is utilized and only meaningful deviations are recorded. Having examined each of the guide words for each of the properties relevant to this part of the system, another part (say the transfer line for material B) would be selected and the process repeated. Eventually all parts of the system would be examined in this manner and the results recorded.
...
Table B.2 – Example HAZOP worksheet for introductory example
[...]
Table B.3 – Example HAZOP worksheet for procedures example
[...] Segue in allegato
Certifico Srl - EN | Rev. 0.0 2022
©Copia autorizzata Abbonati
Fonte: IEC 61882:2016: HAZOP
Collegati