Dispositivi di comando a due mani: EN ISO 13851:2019
ID 8883 | 05 Agosto 2019
Documento estratto dalla norma EN ISO 13851:2019 - Sicurezza del macchinario - Dispositivi di comando a due mani - Principi per la progettazione e la scelta che specifica i requisiti di sicurezza di un dispositivo di comando a due mani (THCD) e la dipendenza del segnale di uscita dall'azionamento manuale dei dispositivi di azionamento.
UNI EN ISO 13851:2019 Sicurezza del macchinario - Dispositivi di comando a due mani - Principi per la progettazione e la scelta
Data entrata in vigore: 04 luglio 2019
Il presente documento descrive le caratteristiche principali dei dispositivi di controllo a due mani per garantire la sicurezza e stabilisce combinazioni di caratteristiche funzionali per tre tipi. Essa non si applica ai dispositivi destinati ad essere utilizzati come dispositivi di convalida, come dispositivi di comando ad azione mantenuta o come dispositivi di controllo speciali.
Recepisce: EN ISO 13851:2019
Adotta: ISO 13851:2019
Sostituisce: UNI EN 574:2008
http://store.uni.com/catalogo/index.php/uni-en-iso-13851-2019.html
Con la Decisione di esecuzione (UE) 2021/377 (GU L 72/12 del 3.3.2021), la norma è entrata in regime di armonizzazione per la Direttiva macchine 2006/42/CE.
...
Le macchine devono essere progettate in modo tale che le protezioni utilizzate per la sicurezza possano garantire protezione agli addetti alla produzione, manutenzione, riparazione e pulizia, senza ostacolare lo svolgimento del lavoro. Ci sono situazioni in cui è necessario che l’operatore acceda alla zona pericolosa durante la lavorazione; in questi casi si devono prendere misure di sicurezza alternative: sulla macchina dovranno essere installati mezzi adeguati che riducano il rischio e che utilizzino il comando manuale (UNI EN ISO 12100:2010), tra cui anche i dispositivi di comando a due mani, per autorizzare il funzionamento degli elementi pericolosi.
I comandi a due mani possono essere efficacemente utilizzati quali dispositivi di protezione per l'operatore, in quanto lo costringono a tenere le mani sui comandi e quindi fuori dalle zone pericolose.
Perché i comandi a due mani siano un mezzo di protezione efficace è necessario che siano soddisfatti alcuni requisiti:
- devono essere mantenuti azionati finché le condizioni pericolose sono terminate; per esempio, nel caso di una pressa meccanica, i comandi a due mani devono essere mantenuti azionati finché termina la fase di discesa della mazza, mentre, durante la fase di risalita, possono normalmente essere rilasciati.
- è fondamentalmente raccomandato di curare la loro collocazione, l’eventuale combinazione con altre protezioni, l’aspetto della regolazione, che deve sempre richiedere un intervento volontario, e la garanzia di disponibilità della funzione di sicurezza, anche in caso di guasto.
La norma di tipo B di riferimento per i comandi a due mani è la EN ISO 13851:2019 Sicurezza del macchinario - Dispositivi di comando a due mani - Principi per la progettazione e la scelta; essa specifica i requisiti di sicurezza di un dispositivo di comando a due mani (THCD) e la dipendenza del segnale di uscita dall'azionamento manuale dei dispositivi di azionamento.
Il presente documento descrive le caratteristiche principali dei dispositivi di controllo a due mani per garantire la sicurezza e stabilisce combinazioni di caratteristiche funzionali per tre tipi. Essa non si applica ai dispositivi destinati ad essere utilizzati come dispositivi di convalida, come dispositivi di comando ad azione mantenuta o come dispositivi di controllo speciali.
________
Excursus
Selection, design and installation of control actuating devices
Control actuating devices shall be selected, designed, arranged and installed in such a way that they can be actuated without undue fatigue (e.g. as a result of awkward posture, unsuitable movements or high operating forces) (see ISO 9355-3).
Control actuating devices shall not b2 red.
Control actuating devices shall not form any crushing or shell ring points with any other parts.
The THCD and its interconnection(s) shall be designed and integrated to comply with the
functional safety requirements according to ISO 13849-1 or IEC 62061 (for THCD see Table 1).
Prevention of unintended output signals by acceleration forces
Foreseeable forces caused by acceleration imparted to the THCD shall not cause an output signal (e.g. falling over, accidental impact or shockloading).
Unintended operation of hand-held machines
A THCD shall be designed to prevent unintended operation due to handling.
A THCD shall be designed so that separate and dissimilar actions of the control actuating devices are required to give the input signal to start the dangerous motion of the machine.
NOTE 1 The provision of the two control actuating devices in separate handles does not satisfy this requirement unless their method of operation is different.
NOTE 2 The provision of an automatic lock-out facility on one of the control actuating devices provides a higher level of protection.
Relocatable THCDs
The actuators of a relocatable THCD and their supporting enclosure shall be stable in intended use (see ISO 12100).
NOTE This can be fulfilled by including a large mass or any other suitable means.
Relocatable THCDs s hall be provided with means to prevent movement when being operated. If this is not possible, the position of the THCD shall be monitored resulting in that the moving of the THCD during operation shall initiate a cessation of the output signal. The monitoring function of the position shall have the same required PL/SIL as the actual two hand device safety function.
NOTE This can be fulfilled by including a large mass, use of lockable wheels or any other suitable means.
Facilities shall be available for maintaining and verifying the required safety distance between
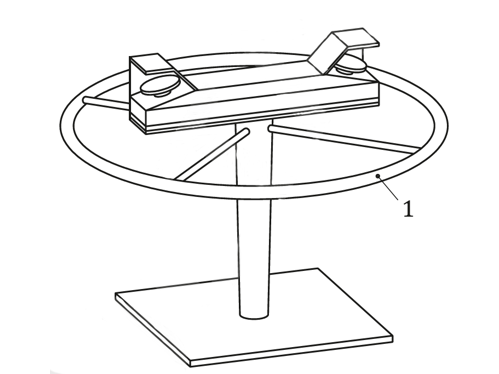
the control actuating devices and the danger zone (e.g. by means of a distance ring see Figure 3).
Figure 3 - Example of a relocatable THCD with a distance ring
Key
1 Distance ring
Pipes, cables and connections shall be protected against damage using the considerations presented in 8.2 and 8.4.4 of the standard.
Safety distance
To calculate the required safety distance (referred to as the minimum distance in ISO 13855) between the control actuating devices and the danger zone, the following shall be taken into account:
- the hand/arm speed (see ISO 13855);
- the shape and arrangement of the THCD;
- the response time of the THCD;
- the maximum time taken to stop the machine, or remove the hazard, following cessation of the output signal of the THCD;
- the intended use and foreseeable misuse of the machine (see ISO 12100);
- relevant type C standards.
Verification and validation
General requirements for verification and validation
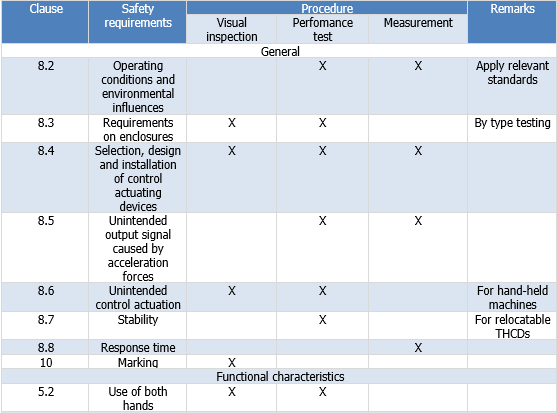
Compliance with the requirements specified for a THCD, shall be verified and validated by visual inspection, theoretical assessment of the design and by practical tests as appropriate. A summary of the verification procedures is given in Table 2.
NOTE Table 2 is not relevant for integrators using pre-assessed THCD.
...[segue in allegato]
Fonti: EN ISO 13851:2019
Certifico Srl - IT | Rev. 00 2019
©Copia autorizzata Abbonati
Collegati: